Introduction
In this three-part blog series, I will guide you through the lineup of functional medicine vs. conventional medicine. I hope to help YOU better understand these healthcare paradigms in a clear and yet comprehensive way!
The harsh reality is that healthcare in the United States is beyond expensive and less than effective on the global stage. This is a fact that has led many Americans to seek information, empowerment, and autonomy alongside the conventional model.
Functional medicine is an emerging paradigm shift within healthcare. Many stumble upon this paradigm in their journey to understanding and digging their feet in!
Consider these recent statistics: In 2022, U.S. health care spending grew 4.1 percent, reaching $13,493 per person and 17.3% of the nation’s Gross Domestic Product.
Additionally, recent data on worsening health outcomes in the United States revealed some staggering details. Our nation has the lowest life expectancy at birth, highest death rates for avoidable and treatable conditions, highest rates of multiple chronic conditions, and so many more unfortunate stats.
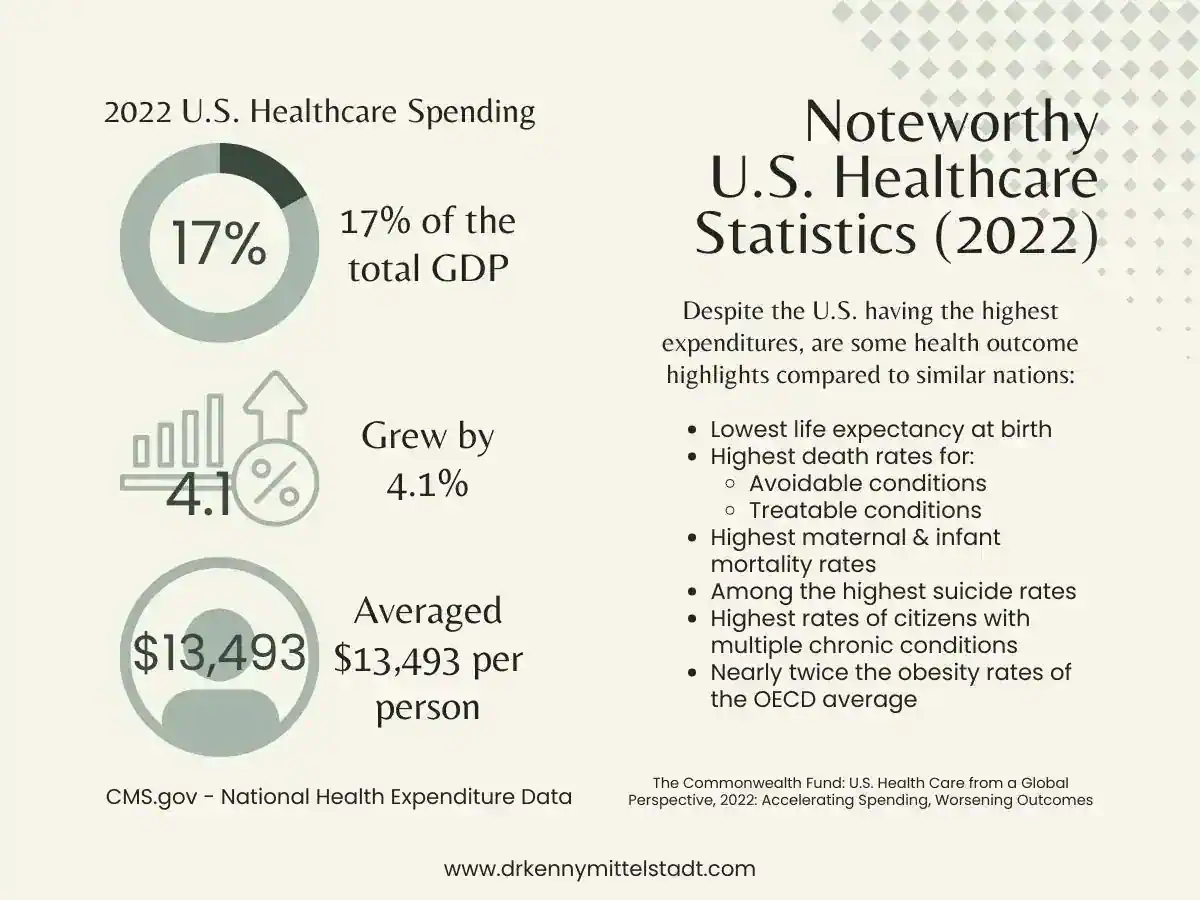
Truly mind-boggling!! Despite spending the absolute most money, we have the absolute lowest health outcomes when compared to similar nations! Frankly, wouldn’t you summarize the healthcare norms and status quo seems to be performing quite poorly?
But what is functional medicine, and how does it compare or relate to conventional medicine?
I believe objective understanding of the terrain is foundational to a way forward – individually and large-scale!
Sounds like a plan? Then, let’s dive right in to this Part 1 of this trifecta exploring functional medicine vs. conventional medicine!
What is Functional Medicine?
The term, functional medicine, was formally coined in 1990 by Dr. Jeffrey Bland and continued to materialize. The conceptual roots of this paradigm were formed earlier in the 20th century.
Functional medicine focuses on identifying underlying causes for disease and dysfunction. The system highlights the importance of personalized treatment. Decisions are based on a comprehensive understanding of the complexities of each and every patient.
It emphasizes lifestyle interventions such as diet, exercise, and stress management in addition to nutraceuticals and herbs when warranted. Functional medicine also uses conventional medicine interventions such as pharmaceuticals and surgery when necessary.
Functional medicine attempts to discover the “why” behind health issues. It then focuses treatment on restoring those functions (thus the name functional medicine) rather than solely focusing on the “what” or the diagnosis.
Finally, it takes a scientific, evidence based approach and recognizes the importance of holistic healing. This includes physical health, mental and emotional health, environmental factors, genetics, and social health among the considerations.
Most functional medicine practitioners receive advanced training or certification after their primary healthcare degree (MD, DO, DC, NP, PA, etc.).
A formal licensure process for functional medicine isn’t required for practitioners. However, there are quality certification programs that attempt to standardize framework and best practices.
A great place to start exploring more about functional medicine through a formal channel is The Institute for Functional Medicine.
Remember, this is just a summary! We’ll elaborate more on each of these concepts in future sections in this blog post series!
What is Conventional Medicine?
Conventional medicine, also known as allopathic or Western medicine, is the healthcare paradigm that dominates the ideology in the United States and around most of the world. Its roots began in the 16th and 17th centuries and continued developing to the present day!
Conventional medicine takes a symptoms-based, algorithmic approach to disease classification (diagnosis) and treatment. It relies on scientific evidence especially in the form of randomized, clinical controlled trials.
Treatment is then based on a symptom or a diagnosis and generally matched to an intervention. Conventional medicine emphasizes the usage of pharmaceuticals and surgery as such primary treatment interventions.
This system also relies on specialities. In this structure, a practitioner focuses on a single organ or system (i.e. cardiology for the heart) and predominantly practices in this area. Patients are managed through networks by being transferred to relevant specialists when necessary.
Finally, the conventional medicine system in the U.S. is also heavily intertwined with major medical insurance and pharmaceutical companies. This relationship plays a role determining research and the development standardized, evidence-based protocols for treatment.
Again, this is just a brief summary of conventional medicine. We’ll explore each concept further in this three-part series!
Let’s begin with an overarching understanding of key differences between these two healthcare paradigms!
7 Highlights of the Differences between Functional Medicine vs. Conventional Medicine
Let’s begin the conversation of functional medicine vs. conventional medicine side-by-side! We’ll start with a zoomed out discussion that highlights 7 key differences between the two paradigms. The image below presents these 7 differences and are explored further below.

1. Ideological Approach to Patient Care
Functional medicine utilizes a holistic, systems-medicine approach while conventional medicine utilizes a reductionist, algorithmic approach. We will elaborate on each of these ideologies in Part 2 of this blog series.
2. Differing Definitions of Prevention
Functional medicine focuses its efforts on optimizing health and the prevention of disease before signs and symptoms show. Prevention involves the early identification of suboptimal function long before a patient reaches a formal conventional disease state.
Though conventional medicine has a similar technique called primary prevention, focus is practically on early detection and screening as prevention. Screening focuses on specific pathological ranges in lab work and findings rather than suboptimal function.
3. Speciality Lab Testing Options
Functional medicine sometimes utilizes more detailed laboratory testing. The purple is to tease out functional dysfunction both before and while disease is present. The focus on specialty lab testing is identifying unique, detailed functions of an individual patient.
Examples of functional medicine specialty lab testing include the following:
- Digestive function and microbiome analysis through functional stool testing
- Genetic testing for gene variances called SNP’s (single nucleotide polymorphisms)
- Salivary hormone testing
- Micronutrient testing
- Heavy metal and environmental toxin testing
- Breath testing
- Urinary metabolite testing
- Additional markers with conventional lab panels
Conventional medicine uses targeted, algorithmic testing, which is often limited by insurance coverages for the masses. The main purpose of lab testing includes screening and analyzing for findings outside predefined “normal ranges.”
4. Treatment Philosophy: Root versus Branch
Functional medicine recognizes symptoms and experiences of disease as manifestations of underlying dysfunction.
Rather than focusing merely on mitigating these end-stage manifestations (branches), it prioritizes identifying and addressing the root cause of disease and dysfunction, from the inside out.
Conventional medicine tends to focus on mitigating or minimizing symptoms and signs of disease rather than highlighting the underlying causes. Treatment is often considered successful when a symptom or sign is muted rather than an underlying cause corrected.
This is a nuanced difference in functional medicine vs. conventional medicine, but hopefully this makes sense! Comment below or reach out through social media if you want to further elaborate on this idea!
5. Emphasis on Proactive versus Reactive Interventions
Functional medicine attempts to identify nuance in dysfunction before disease results. The focus of treatment advice is usually on preventing illness and dysfunction before it happens. Tailored lifestyle, nutrition, and environmental advice are examples of go-to interventions.
Conventional medicine tends to be more reactive in its approach to treatment. Generally, before a conventional practitioner intervenes with treatment, symptoms and signs must be present.
6. Emphasis on Lifestyle Change as Treatment
Functional medicine recognizes that a majority of chronic disease that we face in contemporary society is largely preventable through nutrition, movement, stress management, and other lifestyle and behavioral modification. As such, it emphasizes these means of treatment.
Conventional medicine primarily relies on treating chronic disease with medication, surgery, and limited nutrition advice. It attempts to change the body through external, passive interventions rather than internal, active interventions.
7. Affinity for Chronic Disease versus Acute, Emergent Care
Functional medicine is aptly posed to address chronic complex illness through a holistic, systems-medicine approach. Such conditions may include obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune conditions, some cancers and many more.
Conventional medicine is unmatched in its powerful management of acute and emergent conditions. In situations such as trauma, heart attack, stroke, surgery, and many more, conventional medicine stands out as a true and fascinating powerhouse!
Conclusion of Functional Medicine vs. Conventional Medicine – Part 1
The current state of our healthcare system is alarming to many, and you’re not alone. We feel the pressure individually as patient, in hospital systems, as practitioners, and in the complementary and alternative medicine world!
To summarize, functional medicine takes a holistic, systems-medicine approach to patient care. It emphasizes lifestyle interventions to address the root-cause of disease and dysfunction.
In contrast, conventional medicine takes a reductionist, scientific, and algorithmic approach to patient care. It emphasizes drugs and surgery as primary interventions to address branch symptoms and signs.
Does this exploration functional medicine vs. conventional medicine intrigue you? If so, I would love for you to stay tuned! Keep reading for Parts 2 and 3 of this discussion!
In Part 2, we’ll dive into more details. We’ll discuss 7 key principles of both the functional medicine and conventional medicine paradigms. In Part 3, we’ll explore criticisms and limitations of each paradigm and explore FAQ’s around the topics!
Again, I hope this introduction of conventional medicine vs. functional medicine brings a sense of understanding and ultimately empowerment! Our health and our sense of power and strength, begins with inward understanding, and I hope this delivers!
Feel free to comment below, contact me, or reach out via Instagram to connect with me! I look forward to sharing more and am here if you have any questions.
“Health is contagious, share the love.” If this post resonates with you, share with a friend or family member! Spark those meaningful conversations around health creation and empowerment!
About the Author
Dr. Kenny Mittelstadt is a root-cause health detective and functional medicine practitioner practicing in Texas, California, and Florida. Trained through the Institute for Functional Medicine with dual doctorates earned at highest honors from Southern California University of Health Sciences, he helps patients solve complex health issues naturally using advanced functional lab testing and personalized holistic care instead of conventional medications.

